Hazard effect management process
Hazard and Effect Management Process (HEMP) is a risk management process which ensures that Hazards/Risks to workforce, equipments, properties and environments are properly controlled. In cases of failure in controls, it helps manage the impacts of incidents as well.
The Hazards and Effects Management Process (HEMP) identifies and assesses HSE hazards, implements control and recovery measures, and maintains a documented demonstration that major HSE risks have been reduced to a level that is As Low As Reasonably Practicable (ALARP).
The tools and techniques available are applied in a logical and rigorous way, setting acceptance criteria and screening against them as the process proceeds. The arrangements identified as necessary to manage assessed threats and potential consequences and effects are then incorporated in the design phase or for existing operations it is necessary to verify that what is in place is suitable and sufficient. If not, then remedial action is taken and all necessary procedures are incorporated into the HSE Management System.
The principles of 'identify', 'assess', 'control' and 'recover' are the basis of HEMP, with the individual stages summarised in the following steps:
- Identify Hazards and Potential Effects
- Evaluate Risks
- Record Hazards and Effects
- Compare with Objectives and Performance Criteria
- Establish Risk Reduction Measures.
Step 1: Identify Hazards and Potential Effects
Systematically identify the hazards, the threats and potential hazardous events and effects which may affect, or arise from, a company's operation throughout the total life cycle of the operation.
Step 2: Evaluate risks
Systematically evaluate (assess) the risks from the identified hazards against accepted screening criteria, taking into account the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of any consequences to employees, assets, the environment and the public. This includes the risks associated with deviation from limits set for environmental and occupational health hazards.
Step 3: Record hazards and effects
Record all those hazards and effects identified as significant in relation to the screening criteria in Hazards and Effects Register.
Step 4: Compare with objectives and performance criteria
Compare the evaluated risks against the detailed HSE objectives and targets for the project or installation. For all cases these targets must be maintained and be consistent with the Company Policy, and Strategic Objectives. Performance standards at all levels must meet the criteria set in the HSE Case which in turn must comply with the Company's HSE Management System.
Step 5: Establish risk reduction measures
Select, evaluate and implement appropriate measures to reduce or eliminate risks.
Perform a detailed bowtie-based analysis of Major accident hazard (MAH), thereby identifying barriers, safety critical activities, safety critical positions and safety critical equipment....
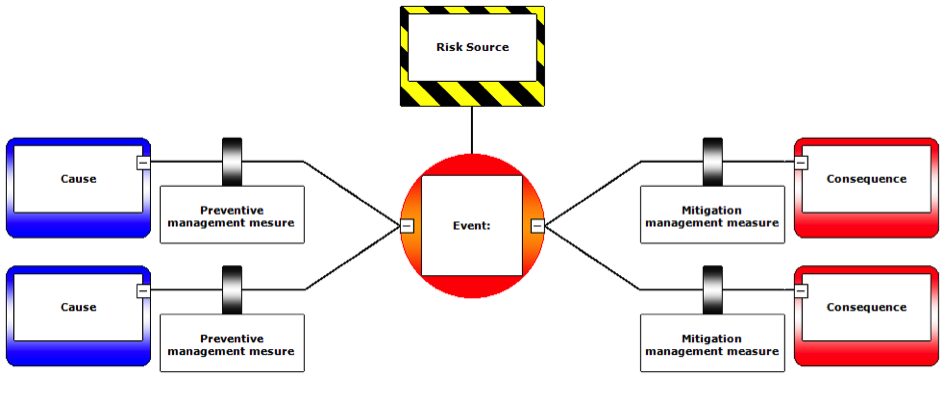 Risk reduction measures include those to prevent or control incidence (i.e. reducing the probability of occurrence) and to mitigate effects (i.e. reducing the consequences). Mitigation measures include steps to prevent escalation of developing abnormal situations and to lessen adverse effects on Health, Safety and the Environment. Risk reduction measures also include recovery preparedness measures which address emergency procedures as well as restoration and compensation procedures to recover.
Risk reduction measures include those to prevent or control incidence (i.e. reducing the probability of occurrence) and to mitigate effects (i.e. reducing the consequences). Mitigation measures include steps to prevent escalation of developing abnormal situations and to lessen adverse effects on Health, Safety and the Environment. Risk reduction measures also include recovery preparedness measures which address emergency procedures as well as restoration and compensation procedures to recover.
Services provided by KTT:
- Consulting, training and implementing HEMP program
- Bowtie analysis for process unit and equipment
- Provide a powerful HEMP management software
